Using hot-add/hot-plug you can add computing resources (RAM/vCPUs) to virtual machines without any downtime.
By default, hot-add/hot-plug is disabled – you have to enable this feature on a per-VM basis using your webclient or vSphere Client (you have to shut down the VM to enable the feature):
How to enable hot-add/hot-plug using the webclient:
- shut down the virtual machine
- login to your webclient
- select the virtual machine
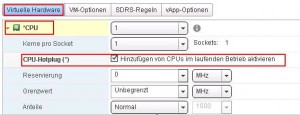
- edit settings – VM Hardware
to enable CPU-hotplug:
- open the CPU Tab
- select: Enable CPU Hot Add
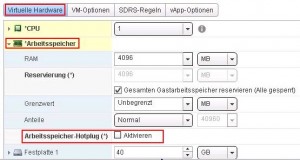
to enable Memory hot-plug:
- open the Memory Tab
- select: Enable Memory Hot Plug
How to enable Hot-add/Hot-plug using the vSphere Client:
- shut down the virtual machine
- login to your vSphere Client
- select the virtual machine
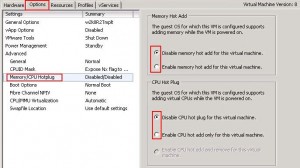
- Edit Settings
- change to the “Options-Tab”
- select Memory/CPU Hotplug
- Enable memory hot add and/or CPU Hot Plug
What are the requirements for Hot-add/Hot-plug:
- minimum Hardware Version 7
- Hot-add/Hot-Plug is not compatible with Fault Tolerance
- vSphere Advanced, Enterprise or Enterprise plus
- only hot-add is possible – you cannot “hot-remove” RAM or vCPUs (but you can of course remove RAM/vCPUs when you shut-down the VM)
- Hot-Add/Hot-plug must be supported by the VM operating system!
- take care of guest-OS licensing limitations when adjusting the number of vCPUs/RAM
Overview Operating System support for Hot-add and Hot-plug:
| Guest Operating System | License | Hot-Add RAM | Hot-Plug CPUs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 32bit/64bit | Standard Enterprise |
||
| Windows Server 2008 32bit | Standard Enterprise Datacenter |
||
| Windows Server 2008 64bit | Standard Enterprise |
||
| Windows Server 2008 64bit | Datacenter | ||
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Standard Enterprise |
||
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Datacenter | ||
| Windows Server 2012 | Standard Datacenter |
If you want to enable Hot-add for a virtual machine with an Windows Server 2003 guest operating system you should read the following KB from Microsoft:
Hot-add vs. vNUMA:
Another point you should take care off is that enabling CPU hot-add will disable ESXi 5.x vNUMA!
There is a KB Article from VMware about this problem: vNUMA is disabled if VCPU hotplug is enabled (2040375)
If you do so, you can see this message in the vmware.log:
vmx| W110: NUMA and VCPU hot add are incompatible. Forcing UMA
What is vNUMA?
vNUMA (virtual non-uniform memory access) is a memory-access optimization method which is automatically enabled for VMs with more than 8 vCPUs.

Please note that hot-add on a Windows Server 2012 (with R2) will crash when you hot-add memory or cpu.
See KB:
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2050800
Very good article. VMware documentation does not mention the limitation with hot-add not supporting hot-remove (I’m not even sure if any guest OS supports hot-remove). Also, it’s worth noting that the vSphere thick client has the option “Enable CPU hot add and remove for this virtual machine” which is not an option in the vSphere Web Client. But in your screenshot the option is grayed out anyway, even in the thick client. I have not tested any of this yet, but plan to.
Hi,
Do we need to power off the VM to enable hot add ??
Any way to enable without shutting down or power off ??